OPEN ACCESS TO THE PAPER

ACCORSI R., VERSARI L., MANZINI R., 2015, Glass vs. Plastic: Life Cycle Assessment of Extra-Virgin Olive Oil Bottles across Global Supply Chains. Sustainability 2015, 7(3), 2818-2840; WOS: 000351843400028. Scopus: 2-s2.0-84926325756. doi:10.3390/su7032818.
Abstract
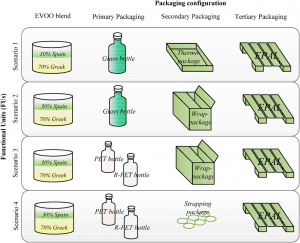
The environmental impacts of global food supply chains are growing with the need for their measurement and management. This paper explores the operations of a global supply chain for extra-virgin olive oil (EVOO) according to a life cycle assessment (LCA) methodology. The LCA assessment methodology is applied to determine the environmental impact categories associated with the bottled EVOO life cycle, focusing on packaging decisions. The proposed analysis identifies the greatest environmental stressors of the EVOO supply chain, thereby supporting strategic and operative decisions toward more efficient and environmentally-friendly operations management and packaging choices. This paper quantifies the environmental categories of the impacts of global warming potential, ozone layer depletion, non-renewable energy use, acidification, eutrophication and photochemical smog, for the observed EVOO supply chain, given alternative packaging configurations, i.e., a glass bottle vs. a plastic bottle. The observed system includes the supply of EVOO, the EVOO processing and bottling, the supply of packaging, the distribution of final products to customers, the end-of-life (EOL) treatments regarding the management, recycling and the disposal of waste across a global supply chain. The findings from the LCA highlight the potential of PET bottles in reducing the environmental impact of EVOO supply chains and identifies hotspots of discussion for policy-makers, EVOO producers and consumers.
Keywords:
food supply chain; life cycle assessment; LCA; sustainability; extra-virgin olive oil; EVOO; recycle; packaging

