
Springer Book on Warehousing
Warehousing in the Global Supply Chain
Advanced Models, Tools and Applications for Storage Systems
Editors: Manzini, Riccardo (Ed.)
With increased globalization and offshore sourcing, global supply chain management is becoming an important issue for many businesses as it involves a company’s worldwide interests and suppliers rather than simply a local or national orientation. The storage systems significantly affect the level of quality of products, the customer’s service level, and the global logistic cost. The mission of warehousing systems design, control and optimization is to effectively ship products in the right place, at the right time, and in the right quantity (i.e. in any configuration) without any damages or alterations, and minimizing costs.
Warehousing in the Global Supply Chain presents and discusses a set of models, tools and real applications, including a few case studies rarely presented with a sufficient detail by other literature, to illustrate the main challenges in warehousing activities. This includes all warehouse operations (from receiving to shipping), problems and issues (e.g. storage allocation, assignment, layout, vehicle routing) for industrial and service systems as parts of global supply chains.
Advanced and effective solving methods are also illustrated and the discussed case studies help the reader to quickly apply the proposed models and techniques/algorithms. Warehousing in the Global Supply Chain is useful to managers and practitioners of industry and service sectors for the determination and modeling of the critical issues concerning warehousing systems planning and design. It is a valuable source of information for engineering students, doctoral and post-doctoral students, and researchers of academic institutions who are searching for advanced modeling approaches and solving techniques to complex logistic decision making problems.
Warehousing in the Global Supply Chain presents and discusses a set of models, tools and real applications, including a few case studies rarely presented with a sufficient detail by other literature, to illustrate the main challenges in warehousing activities. This includes all warehouse operations (from receiving to shipping), problems and issues (e.g. storage allocation, assignment, layout, vehicle routing) for industrial and service systems as parts of global supply chains.
Advanced and effective solving methods are also illustrated and the discussed case studies help the reader to quickly apply the proposed models and techniques/algorithms. Warehousing in the Global Supply Chain is useful to managers and practitioners of industry and service sectors for the determination and modeling of the critical issues concerning warehousing systems planning and design. It is a valuable source of information for engineering students, doctoral and post-doctoral students, and researchers of academic institutions who are searching for advanced modeling approaches and solving techniques to complex logistic decision making problems.







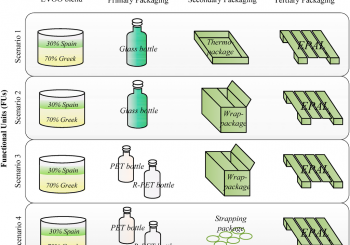

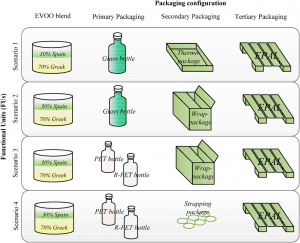









 ► A literature-based discussion of food supply chain. ► The new perspectives and challenges for the future food supply chain management. ► A new conceptual framework for food supply chain assessment. ► A simulation-based analysis of food packaging. ► A case study of international shipment of food from Italy to Taiwan.
► A literature-based discussion of food supply chain. ► The new perspectives and challenges for the future food supply chain management. ► A new conceptual framework for food supply chain assessment. ► A simulation-based analysis of food packaging. ► A case study of international shipment of food from Italy to Taiwan.


 The effects on quality and safety of foodstuffs after transportation process are important for both the producers and the consumers. Herein, a shipment of different bottled vegetable oils (olive oil, extra virgin olive oil and grape seed oils) from Italy to Taiwan, has been simulated within a climate-controlled chamber. The treated samples have been chemically and sensory analyzed, considering basic quality parameters; then, the results were compared with the non-simulated oils from the same production batches. The analyses demonstrate that there is a risk of oxidation due to the shipment to be taken into account
The effects on quality and safety of foodstuffs after transportation process are important for both the producers and the consumers. Herein, a shipment of different bottled vegetable oils (olive oil, extra virgin olive oil and grape seed oils) from Italy to Taiwan, has been simulated within a climate-controlled chamber. The treated samples have been chemically and sensory analyzed, considering basic quality parameters; then, the results were compared with the non-simulated oils from the same production batches. The analyses demonstrate that there is a risk of oxidation due to the shipment to be taken into account
